
Recycling vs. Refurbishing: Choosing the Right Option for Your E-Waste
Did you know approximately 61.3 million metric tons of electronic e-waste was generated globally in 2023? As our dependence on electronic items grows, so does the challenge of responsibly disposing of these gadgets. Whether it’s smartphones, laptops, or tablets, these gadgets have become integral to our daily routines. However, improper disposal of e-waste can have serious environmental and health repercussions. Many electronic devices contain harmful elements like lead, mercury, and cadmium. It’s crucial for individuals and organizations to prioritize recycling & proper disposal methods to minimize the negative impact on our planet and future generations.
Two standard methods for managing e-waste are recycling and refurbishing. While both approaches aim to reduce the environmental impact of electronic waste, they differ in their processes and outcomes. Let’s discuss the differences between recycling and refurbishing and how individuals and businesses can make responsible decisions when disposing of electronic devices.
Distinction Between Recycling & Refurbishing
Recycling E-Waste:
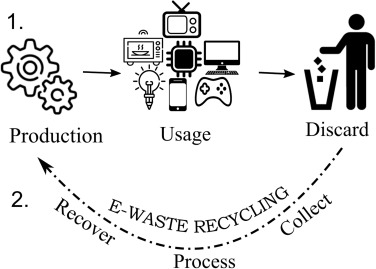
Recycling involves breaking down electronic devices into raw materials, such as metals, plastics, and glass, which can be used to manufacture new products. One of the main challenges of e-waste recycling is the complex composition of electronic devices, which contain a mix of materials that are often difficult to separate. Additionally, inadequate infrastructure and lack of awareness can hinder proper collection and recycling efforts. The recycling process typically includes:
Collection: E-waste is collected from individuals, businesses, and electronic manufacturers through designated drop-off points or recycling programs.
Sorting: E-waste is sorted after collection based on the type of material and its condition. Metals and plastics that can be recycled are separated from materials that cannot be recycled.
Processing: Recyclable materials are processed using various techniques, including shredding, melting, and refining, to extract valuable raw materials.
Manufacturing: The recovered materials are then used to manufacture new electronic devices or other products, closing the loop in the recycling process.
Recycling e-waste helps conserve natural resources, reduces energy consumption, minimizes the amount of waste sent to landfills or incinerators, and prevents harmful chemicals and heavy metals from contaminating soil and water sources. However, not all electronic devices are suitable for recycling, especially if they are outdated or damaged beyond repair.
Refurbishing E-Waste:
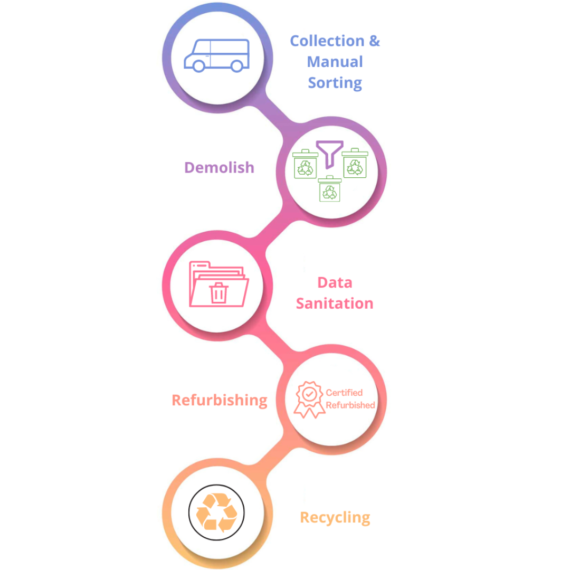
Refurbishing involves repairing and restoring used electronic devices to a functional condition for resale or donation. It extends the lifespan of electronic devices, thereby reducing the demand for new products and minimizing e-waste generation. It also prevents usable devices from ending up in landfills prematurely. This process requires skilled technicians and quality control measures to ensure that refurbished devices meet safety and performance standards. Moreover, consumer perceptions about refurbished products and concerns about warranty and reliability may deter some individuals from choosing refurbished options. The refurbishment process typically includes:
Assessment: Electronic devices are assessed to determine their condition and functionality. It includes inspecting hardware components, testing software performance, and identifying any issues or defects.
Repair: Damaged or faulty components are repaired or replaced to restore the device to working condition. It involves replacing screens, batteries, or other internal parts.
Testing: Refurbished devices go through rigorous testing to meet quality standards and perform as intended. It includes testing hardware functionality, software compatibility, and overall performance.
Repackaging: Once refurbished, the devices are cleaned, sanitized, and repackaged with appropriate accessories before being reintroduced to the market.
Refurbished electronics offer a cost-effective and sustainable alternative to purchasing new devices.
By refurbishing e-waste, we conserve valuable components and materials and reduce the overall environmental footprint associated with responsible electronic consumption. Moreover, refurbishment creates job opportunities in the repair and refurbishment industry that contribute to economic growth and sustainability.
Make The Right Choice Between Recycling & Refurbishing
When it comes to managing e-waste effectively, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions by considering the following tips:
Evaluate the Condition: Assess whether your electronic device can be recycled or refurbished by considering its condition, functionality, and age. Devices with minimal damage or functional problems can be refurbished, whereas outdated or irreparable gadgets should be recycled.
Research Recycling Programs: Look for reputable e-waste recycling programs or facilities that adhere to environmental and safety standards to ensure responsible disposal. Look for certifications such as R2 (Responsible Recycling) or e-Stewards to ensure your e-waste is handled responsibly.
Support Certified Refurbishers: When purchasing refurbished electronics, support refurbishers who follow industry best practices for testing, repairing, and sanitizing devices. Look for warranties and quality guarantees to ensure a reliable product.
Donate or Sell: Explore options to donate or sell your used electronic devices to organizations or individuals who can benefit from them, extending their lifespan and reducing waste.
Data Security: Prioritize data security by securely wiping personal information from devices before disposal or refurbishment to protect privacy.
Promote E-Waste Awareness: Educate others about the importance of proper e-waste management and encourage them to recycle or refurbish their old electronics. Participate in community e-waste collection events or advocacy campaigns to raise awareness and promote sustainability.
Final say!
By choosing to recycle or refurbish e-waste, individuals and businesses can contribute to environmental conservation efforts and reduce their carbon footprint. Together, we can positively impact the planet by embracing responsible e-waste management practices and adopting sustainable consumption habits. Let’s work towards a future where electronic devices are innovative, convenient, environmentally friendly, and socially responsible.
Read Our More Blogs:
Top 5 Things Businesses Need to Do to Comply with E-waste Management Rules
What Can and Can’t Be Recycled in E-Waste
Follow us:







