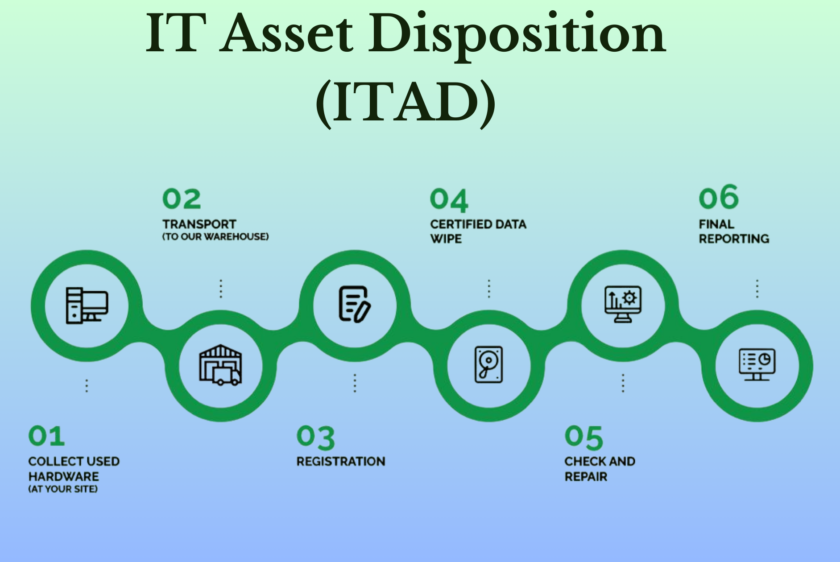
Importance of Responsible IT Asset Disposition (ITAD) for Businesses
Businesses rely heavily on technology in the digitally driven world to drive efficiency, innovation, and growth. However, the rapid pace of technological advancement also means that businesses must continually upgrade and replace their IT assets to stay competitive. This constant cycle of asset turnover raises a critical question: What happens to the old IT equipment when it’s time for an upgrade?
This is where IT Asset Disposal (ITAD) comes into play—the process of properly disposing of outdated IT equipment in a secure, environmentally friendly, and socially responsible manner. However, as organizations upgrade their IT infrastructure to stay competitive, they often overlook the importance of responsibly managing the disposal of outdated equipment. Let’s explore why responsible ITAD is essential for companies and provide best practices to help them make informed decisions.
ITAD: What is it, and Why Does it Matter?
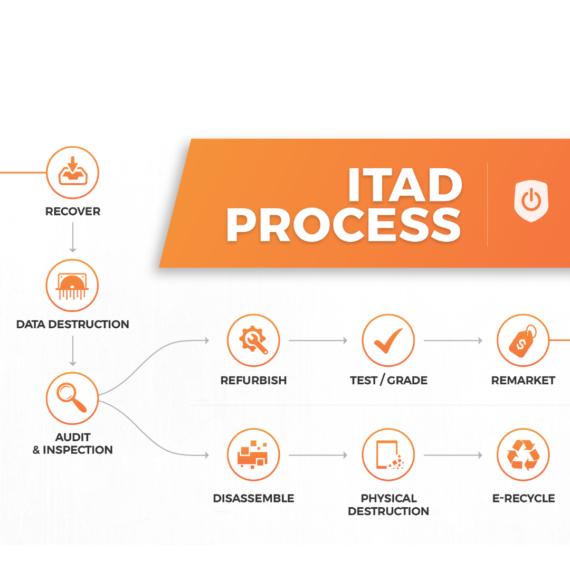
ITAD refers to the secure disposal of retired or obsolete IT assets, such as computers, servers, smartphones, and networking equipment. It involves data sanitization, recycling, refurbishment, or resale of these assets in an environmentally friendly and secure manner.
• Data Destruction: Ensuring all sensitive information is permanently removed from storage devices to prevent data breaches.
• Resale: Refurbishing and reselling usable equipment to extend its life cycle.
• Recycling: Extracting valuable materials from old equipment for reuse in new products, minimizing environmental impact.
• Responsible Disposal: Safely dismantle and dispose of unusable equipment according to environmental regulations.
Here’s why responsible ITAD should be a top priority for businesses of all sizes:
1. Environmental Impact: Electronic waste (e-waste) is a growing concern worldwide, with millions of tons of electronic equipment discarded each year. Irresponsible disposal of IT assets contributes to environmental pollution, resource depletion, and health hazards. Responsible ITAD practices, such as recycling and proper disposal of electronic waste, help minimize the environmental impact and promote a circular economy.
2. Data Security: Protecting sensitive data is paramount for businesses in today’s interconnected world. Improper disposal of IT assets can lead to data breaches, identity theft, and regulatory non-compliance. Responsible ITAD involves thorough data sanitization or destruction procedures to ensure that sensitive information is securely wiped from devices before disposal, mitigating the risk of data breaches.
3. Regulatory Compliance: Many jurisdictions have strict regulations governing the disposal and recycling of electronic waste, as well as data privacy and security standards. Non-compliance with these regulations can result in hefty fines, legal liabilities, and damage to a company’s reputation. Responsible ITAD practices help businesses navigate complex regulatory landscapes and ensure compliance with relevant laws and standards.
4. Resource Efficiency: ITAD allows businesses to recover valuable resources from old IT assets through refurbishment, reuse, or recycling. By extending the lifespan of IT equipment and minimizing waste generation, companies can reduce their environmental footprint and optimize resource utilization.
5. Cost Efficiency: Proper management of IT assets throughout their lifecycle can lead to cost savings for businesses. Companies can recoup some of their initial investment by refurbishing and reselling retired equipment or repurposing components. Additionally, reducing the frequency of equipment replacement through strategic asset management minimizes long-term spending on IT infrastructure.
Best Practices for Responsible ITAD:
1. Develop an ITAD Policy: Establish a comprehensive ITAD policy that outlines procedures for asset disposal, data sanitization, and environmental stewardship. Ensure all employees are aware of and adhere to the policy to maintain consistency and compliance across the organization.
2. Partner with Certified ITAD Providers: Work with reputable ITAD providers that adhere to industry best practices and hold certifications such as e-Stewards, R2 (Responsible Recycling), or ISO 14001. These certifications ensure that ITAD providers follow strict environmental and data security standards.
3. Implement Secure Data Destruction: Prioritize data security by implementing secure data destruction methods, such as disk wiping, degaussing, or physical destruction, depending on the sensitivity of the data. Verify that data destruction processes comply with relevant data protection regulations.
4. Maximize Asset Value: Explore options to maximize the value of retired IT assets through refurbishment, resale, or donation. By extending the useful life of IT equipment, businesses can generate revenue, reduce disposal costs, and contribute to social responsibility initiatives.
5. Track and Audit IT Assets: Maintain accurate records of IT assets throughout their lifecycle, including procurement, deployment, and disposal. Implement asset tracking systems and conduct regular audits to ensure transparency, accountability, and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Final say!
Responsible IT Asset Disposition (ITAD) is a critical component of effective IT asset management for businesses. Companies can mitigate risks by prioritizing data security, environmental sustainability, legal compliance, cost savings, and fostering a more sustainable digital ecosystem. Implementing best practices for responsible ITAD empowers businesses to make informed decisions regarding their IT asset lifecycle management, ultimately driving long-term success and sustainability.
Read Our More Blogs:
5 Essential Questions to Ask When Hiring an E-Waste Management Service
Best Practices For E-waste Management in the Workplace
Follow us:







