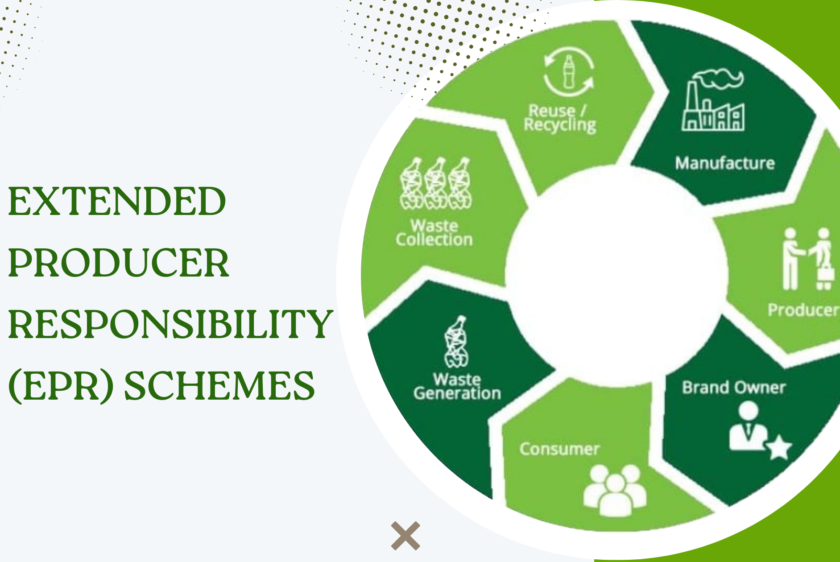
Are EPR schemes effective in reducing e-waste generation?
In a time of rapid technological advancements and the widespread use of electronic devices in our daily lives, the dark side of this progress is the growing challenge of electronic waste (e-waste). Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) schemes offer hope in addressing these issues by placing the responsibility for collecting and properly disposing of electronic products on the manufacturers and encouraging them to design products with end-of-life considerations in mind. In this blog, we will examine their effectiveness in reducing e-waste generation and their impact on the environment.
Impact Of EPR Initiatives on E-Waste Reduction:
EPR schemes play a crucial role in reducing the environmental footprint of electronic devices. By making manufacturers responsible for the disposal of their products, EPR ensures that they are incentivized to design products with longevity and recyclability in mind. This shift in approach discourages the production of disposable electronics, ultimately reducing e-waste generation.
Promoting Sustainable Waste Management:
One of the key benefits of EPR is the promotion of sustainable waste management practices. Manufacturers are encouraged to implement efficient recycling systems, facilitating the recovery of valuable materials from discarded electronics. It conserves precious resources and minimizes the environmental impact associated with traditional waste disposal methods.
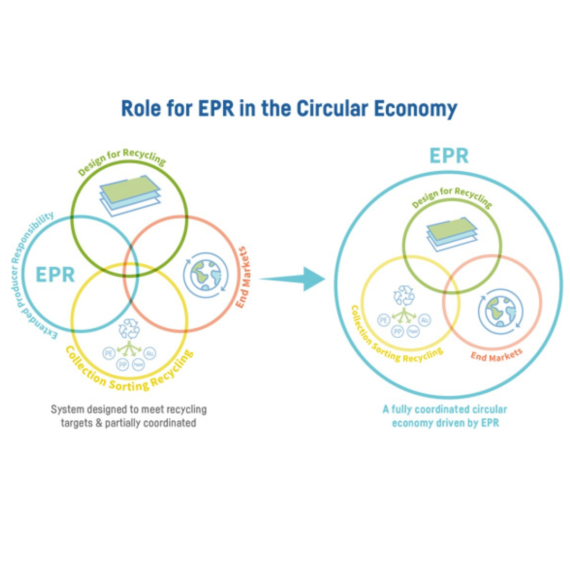
Creating a Circular Economy:
EPR initiatives contribute to the establishment of a circular economy, where products are designed to be reused, refurbished, or recycled. This approach breaks away from the linear “take-make-dispose” model, reducing the extraction of raw materials and lessening the burden on landfills. EPR helps create a more eco-friendly and sustainable electronic consumption cycle by encouraging the reuse of components and materials.
Practical Solutions for Eco-Friendly Electronic Consumptiom:
Product Design Innovation: Manufacturers can prioritize designing products that are easy to disassemble and repair, promoting a culture of reuse and reducing the need for constant upgrades.
Consumer Education: Making consumers aware of the environmental impact of e-waste and the importance of responsible disposal can drive awareness and support for EPR initiatives.
Government Regulations: Governments play a crucial role in shaping the success of EPR programs. Implementing and enforcing regulations that hold manufacturers accountable for their products’ end-of-life management can strengthen the effectiveness of EPR.
Collaboration and Partnerships: Encouraging collaboration between manufacturers, recyclers, and technology experts can foster innovation in e-waste management solutions and ensure the success of EPR programs.
Conclusion:
As our dependence on electronic devices increases, the need for effective e-waste management becomes increasingly urgent. Extended Producer Responsibility schemes offer a promising solution by shifting the burden from consumers to manufacturers. By exploring the impact, implementation, and challenges of EPR initiatives, we can work towards building a more sustainable and eco-friendly electronic consumption landscape. Through collective efforts, we can bridge the gap for a greener future where electronic waste is minimized, and resources are conserved for future generations.
Follow us:







